Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
Nilotinib (AMN107) is a second-generation Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor with antineoplastic activity.
| パッケージサイズ | 在庫状況 | 単価(税別) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| サンプルについてお問い合わせ | |||||
| 50 mg | 在庫あり | ¥ 8,000 | |||
| 100 mg | 在庫あり | ¥ 10,000 | |||
| 200 mg | 在庫あり | ¥ 11,500 | |||
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | 在庫あり | ¥ 11,500 | |||
| 説明 | Nilotinib (AMN107) is a second-generation Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor with antineoplastic activity. |
| ターゲット&IC50 | Abl (WT):15 nM (cell free) |
| In vitro | Nilotinib (AMN107) inhibited Abl-catalyzed peptide substrate phosphorylation with ~20-fold higher potency than imatinib (IC50: 15 versus 280 nmol/L). AMN107 inhibited the growth of cells expressing wild-type Bcr-Abl with 20-fold higher potency than imatinib (IC50: 13 versus 260 nmol/L) [1].Parent and imatinib-resistant GIST cell lines showed sensitivity to nilotinib in a concentration-dependent manner with the IC50 values of parent GIST cell lines being 3.15±0.31 μM for GK1C and 3.32±0.18 μM for GK3C (n.s.), and the imatinib-resistant cell lines showing IC50 values of 4.10±0.46 μM and 3.96±0.19 μM for GK1C-IR and GK3C-IR (n.s.), respectively [2]. Nilotinib inhibited proliferation, migration, and actin filament formation, as well as the expression of α-SMA and collagen in activated HSCs. Nilotinib induced apoptosis of HSCs. Nilotinib also induced cell cycle arrest, accompanied by increased expression of p27 and downregulation of cyclin D1 [3]. |
| In vivo | The percentage of tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was 69.6% for nilotinib in the GK1X xenograft line. In the GK2X xenograft line, TGI was 85.3% for nilotinib [2]. Imatinib and nilotinib attenuated the extent of lung injury and fibrosis. The numbers of inflammatory cells and levels of IL-6, IL-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α were decreased in the imatinib and nilotinib groups on days 3 and 7. Imatinib and nilotinib therapy significantly reduced the levels of hydroxyproline on days 14 and 21, which was accompanied by decreased expression levels of TGF-β1 and PDGFR-β [4]. |
| キナーゼ試験 | Kinase assays using wild-type and mutant glutathione S-transferase (GST)–Abl fusion proteins (c-Abl amino acids 220-498) were done as described, with minor alterations. GST-Abl fusion proteins were released from glutathione-Sepharose beads before use; the concentration of ATP was 5 μmol/L. Immediately before use in kinase autophosphorylation and in vitro peptide substrate phosphorylation assays, GST-Abl kinase domain fusion proteins were treated with LAR tyrosine phosphatase according to the manufacturer's instructions. After 1-hour incubation at 30°C, LAR phosphatase was inactivated by addition of sodium vanadate (1 mmol/L). Immunoblot analysis comparing untreated GST-Abl kinase to dephosphorylated GST-Abl kinase was routinely done using phosphotyrosine-specific antibody 4G10 to confirm complete (>95%) dephosphorylation of tyrosine residues and c-Abl antibody CST 2862 to confirm equal loading of GST-Abl kinase. The inhibitor concentration ranges for IC50 determinations were 0 to 5,000 nmol/L (imatinib and AMN107) or 0 to 32 nmol/L (BMS-354825). The BMS-354825 concentration range was extended to 1,000 nmol/L for mutant T315I. These same inhibitor concentrations were used for the in vitro peptide substrate phosphorylation assays. The three inhibitors were tested over these same concentration ranges against GST-Src kinase and GST-Lyn kinase [1]. |
| 細胞研究 | Ba/F3 cell lines were plated in triplicate and incubated with escalating concentrations of imatinib, AMN107, or BMS-354825 for 72 hours. Proliferation was measured using a methanethiosulfonate-based viability assay. IC50 and IC90 values are reported as the mean of three independent experiments done in quadruplicate. The inhibitor concentration ranges for IC50 and IC90 determinations were 0 to 2,000 nmol/L (imatinib and AMN107) or 0 to 32 nmol/L (BMS-354825). The imatinib concentration range was extended to 6,400 nmol/L for mutants with IC50 >2,000 nmol/L. The BMS-354825 concentration range was extended to 200 nmol/L for mutant T315I [1]. |
| 動物実験 | The GIST xenograft lines GK1X, GK2X and GK3X in nude mice were established from GIST patients as described in our previous study [10]. These xenograft lines were maintained by continual passage in BALB/cSLc-nu/nu mice. Mice bearing GK1X, GK2X and GK3X tumors (6–8 mice per group) were treated daily with vehicle or 40 mg/kg imatinib or nilotinib for 4 weeks. Tumor volume (TV) was determined from caliper measurements of tumor length (L) and width (w) according to the formula LW2/2. TV was determined every two to three days and on the day of evaluation. Mice were sacrificed and the percentage of tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was calculated as follows: TGI (%) ?=? [1– (mean of treatment group tumor volume on evaluation day – mean of treatment group tumor volume on day 1)/(mean of control group tumor volume on evaluation day – mean of control group tumor volume on day 1)]×100 [2]. |
| 別名 | Tasigna, AMN107 |
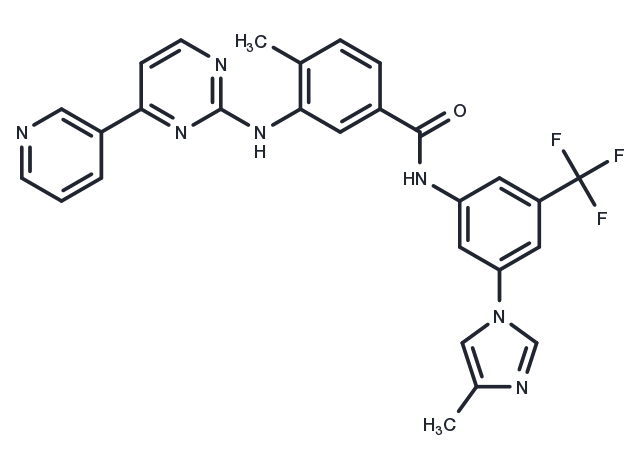
| 分子量 | 529.52 |
| 分子式 | C28H22F3N7O |
| CAS No. | 641571-10-0 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble)
Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble)
DMSO: 26 mg/mL (49.1 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. 詳細
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Nilotinib 641571-10-0 Angiogenesis Autophagy Cytoskeletal Signaling Tyrosine Kinase/Adaptors Bcr-Abl antitumor AMN-107 AMN 107 tyrosine kinase Inhibitor Tasigna inhibit AMN107 inhibitor
